KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!







Researchers have discovered a set of previously unknown methods to launch URL redirection attacks against weak OAuth 2.0 implementations.
These attacks can lead to the bypassing of phishing detection and email security solutions, and at the same time, gives phishing URLs a false snse of legitimacy to victims.
The relevant campaigns were detected by Proofpoint, and target Outlook Web Access, PayPal, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace.
OAuth 2.0 is a widely adopted authorization protocol that allows a web or desktop application access to resources controlled by the end-user, such as their email, contacts, profile information, or social accounts.
Also Read: This Educator Aims to Make Good Cyber Hygiene a Household Practice
This authentication feature relies on the user granting access to a particular application, which creates an access token that other sites can use to access a user’s resources.
When developing OAuth apps, developers are given the freedom to select among various available flow types, depending on their needs, as illustrated below.
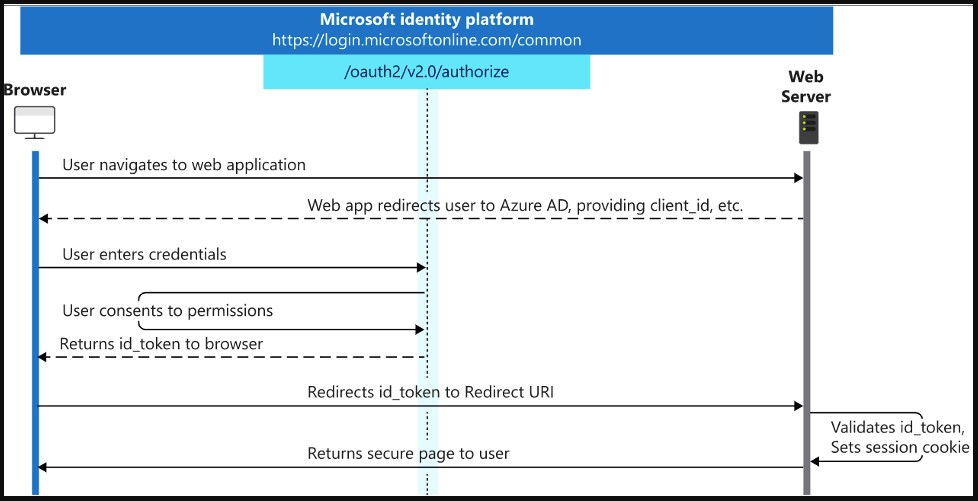
These flows require app developers to define specific parameters, such as a unique client ID, scope, and a redirect URL is opened after successful authentication.
However, Proofpoint discovered that attackers could modify some of the parameters in valid authorization flows, triggering a redirection of the victim to an attacker-supplied site or redirect URL in a registered malicious OAuth app.
Since this happens after the victim has clicked a legitimate-looking URL belonging to Microsoft, the victim falsely assumes that the URL is legitimate, even though they are being redirected to a malicious site.
This redirection can be triggered by modifying the ‘response_type’ query parameter to contain an invalid value, and the victim is taken to a phishing page by Microsoft after authentication.
The same happens if the ‘scope’ parameter is edited to trigger an “invalid_resource” error.
Also Read: Vulnerability Management For Cybersecurity Dummies

“The attacks use dozens of distinct Microsoft 365 third-party applications with malicious redirect URLs defined for them,” explains Proofpoint’s report
“All the third-party applications were being delivered through a Microsoft URL with a missing response_type query parameter, with the intention to redirect unsuspecting users to different phishing URLs.”
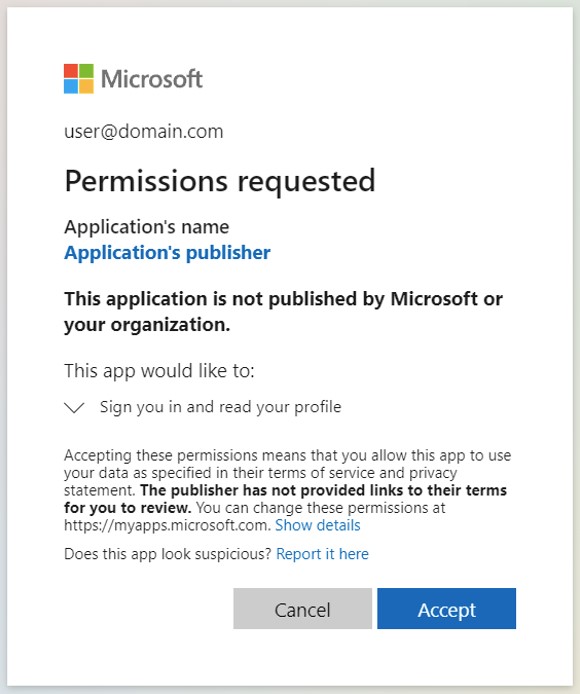
The third attack scenario is the user clicking on the Cancel button at the consent screen, which triggers a redirect to the malicious application URL.
Proofpoint explains that triggering the redirection even before the authentication is also possible, depending on what OAuth flow was selected, which is the case with Azure Portal.
By using OAuth URLs that have been modified to produce errors in the authentication flow, phishing campaigns can present legitimate-looking URLs that ultimately redirect to landing pages that attempt to steal login credentials.
These attacks are not theoretical, as Proofpoint has seen examples in the wild of threat actors abusing this bug to redirect users to phishing landing pages.
“We analyzed Proofpoint data and found large-scale targeted attacks using modi operandi (MOs), which we’ll discuss in detail later in this blog post. The attacks use dozens of distinct Microsoft 365 third-party applications with malicious redirect URLs defined for them.
“They’ve successfully targeted hundreds of users of Proofpoint customer tenants, and the numbers keep growing daily,” explained Proofpoint researchers David Krispin and Nir Swartz.
Other OAuth providers are affected by similar bugs that make it easy to create trustworthy URLs that redirect to malicious sites.
For example, GitHub allows anyone to register an OAuth app, including threat actors who create apps whose redirect URLs lead to phishing landing pages.
Threat actors can then create OAuth URLs containing legitimate-looking redirect URLs, which GitHub ignores and instead uses the redirect defined by the app. To the user, though, the URL looks legitimate and will appear trustworthy to click.
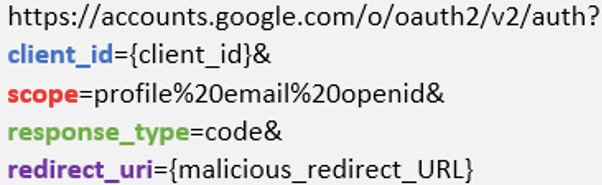
Google makes it even easier as a threat actor can register a sign-in OAuth application and set a ‘redirect_uri’ parameter to a malicious URL, taking the victim there right after authentication.
Google does not verify this URL, so it could be anything, from a phishing page to a malware-dropping site.
Proofpoint’s report provides multiple mitigation techniques for these bugs, with the most effective being not to ignore invalid parameters and instead display an error page.
Also, implementing a long delay before automatic redirection or introducing an additional click for the redirection to take place would save many from getting phished.
“Phishing innocent users remains the most successful attack method to compromise user credentials and breach your organization’s network in the process. Email protection systems are helpless against these attacks,” concludes Proofpoint.
“By abusing OAuth infrastructure, these attacks deliver malicious emails to their targets undetected. Such attacks on PayPal can lead to theft of financial information such as credit cards. Phishing attacks on Microsoft can lead to fraud, intellectual property theft and more.”
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) provides additional security recommendations for those who implement authentication OAuth servers.