KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!







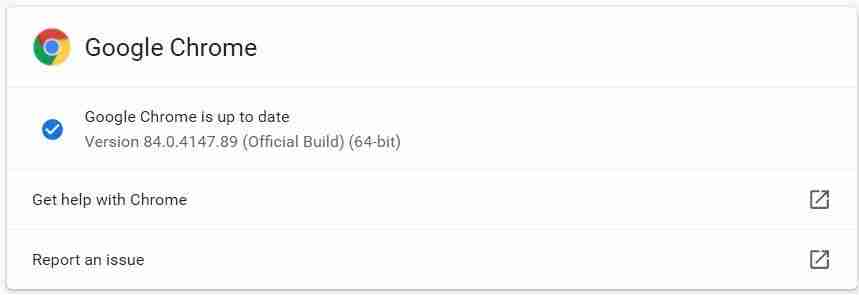
Google has released Chrome 84 today, July 14th, 2020, to the Stable desktop channel, and it includes numerous security enhancements and new APIs for developers.
This massive release does not include many new features but offers increased protection against browser notification scams, mixed-content downloads, and the removal of insecure TLS protocols.
With Chrome 84 now being promoted to the Stable channel, Chrome 85 will soon be promoted to the Beta version, and Chrome 86 will be the Canary version.
Windows, Mac, and Linux desktop users can upgrade to Chrome 84 by going to Settings -> Help -> About Google Chrome. The browser will then automatically check for the new update and install it when available.
In a coordinated announcement in 2018, Microsoft, Google, Apple, and Mozilla stated that they were removing support for the TLS 1.0 and 1.1 secure communication protocols beginning in 2020.
Google planned on removing support for these protocols in Chrome 81. However, due to the Coronavirus pandemic, the protocol’s removal was delayed so that users would still be able to access health and government sites that may be using older certificates.
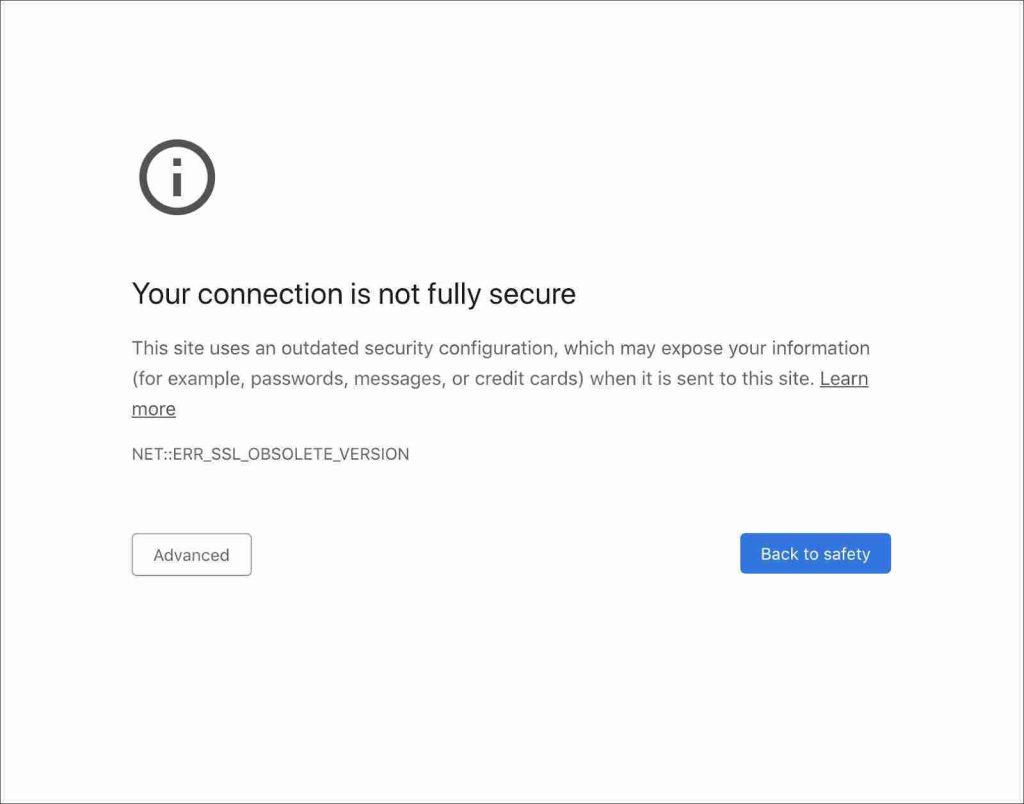
With Chrome 84, Google is now removing TLS 1.0 and 1.1 support.
When visitors access a site utilizing these older certificates, they will be greeted with a full-page interstitial page stating that the “Your connection is not fully secure,” as shown below.
Chrome Enterprise customers can enable TLS 1.0 and 1.1 support until January 2021 through the use of the Chrome group policies.
Also read: Top 10 Reliable IT Companies in Singapore
In April 2019, we reported that Google planned to block mixed content downloads, which are files delivered over insecure HTTP connection when they are first initiated from HTTPS websites.
In previous versions of Google Chrome, Google had displayed errors in the console when these types of downloads were initiated.
With this release, Chrome will now display a visual warning when a mixed-content download is initiated that states the file “can’t be downloaded securely.”
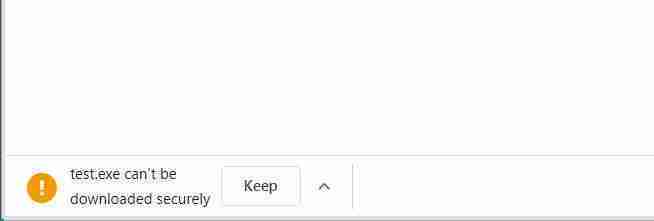
After upgrading to Chrome 84, you can use this BleepingComputer demo page to see the warnings.
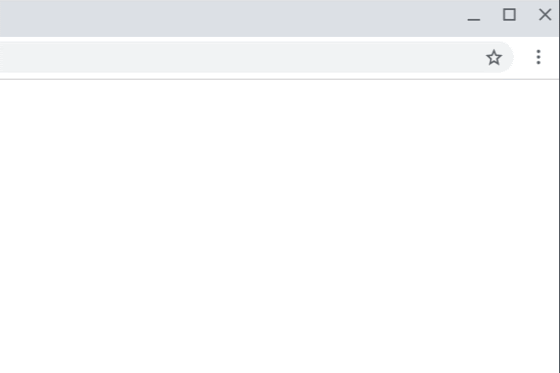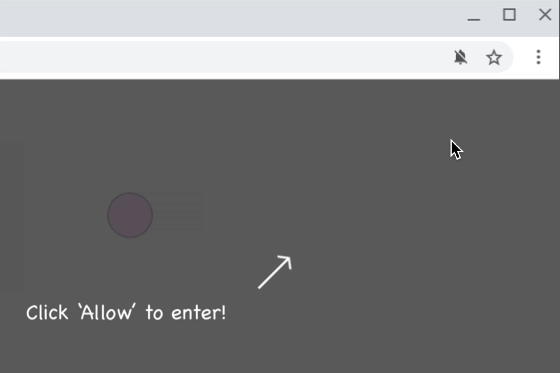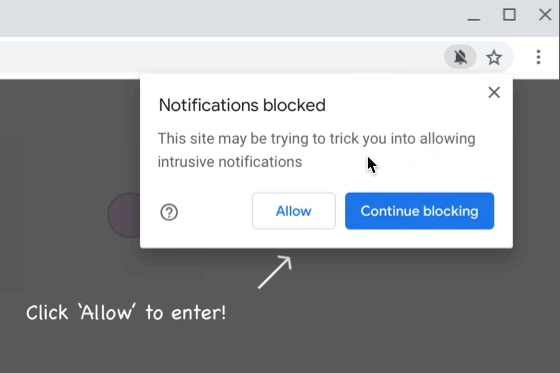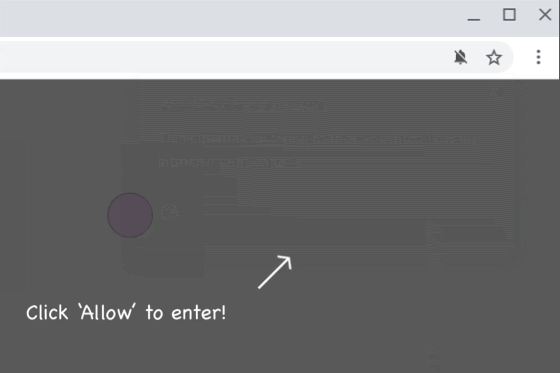
Since 2018, BleepingComputer has been reporting [1, 2] about scam sites tricking users into subscribing to browser notifications,

Once a user accepts these browser notification subscriptions, they will be bombarded with spam for adult dating sites, fake giveaways, unwanted chrome extensions, and even malware.
In 2019, scam browser notification prompts increased by 69%, and Google is now making an effort to stop their proliferation.
With Chrome 84, Chrome will display a warning when a scam site has been detecting that abuses browser notifications.
Chrome 84 comes with numerous new APIs that allow developers to interact with the operating system to a greater degree or increase performance while browsing.
Raw Clipboard Access is a low-level API that allows web applications to correctly copy data to and from native applications that use proprietary file formats.
The QuicTransport API will allow web applications to connect to servers using the QUIC low latency and bi-directional transport protocol.
This protocol allows applications to send and receive data in a reliable and unreliable manner using UDP packets.
Its low-latency approach allows developers to create bi-directional tunnels between a web application and a server with increased performance.
Chrome 84 introduces a new Screen Wake Lock API that prevents a “device from dimming and locking the screen. This capability enables new experiences that, until now, required a native app.”
The Chrome 84 release fixes 38 security vulnerabilities, with the following discovered by external researchers:
| Rating | CVE ID | Description |
| Critical | CVE-2020-6510 | Heap buffer overflow in background fetch. Reported by Leecraso and Guang Gong of 360 Alpha Lab working with 360 BugCloud on 2020-07-08 |
| High | CVE-2020-6511 | Side-channel information leakage in content security policy. Reported by Mikhail Oblozhikhin on 2020-04-24 |
| High | CVE-2020-6512 | Type Confusion in V8. Reported by nocma, leogan, cheneyxu of WeChat Open Platform Security Team on 2020-05-20 |
| High | CVE-2020-6513 | Heap buffer overflow in PDFium. Reported by Aleksandar Nikolic of Cisco Talos on 2020-06-04 |
| High | CVE-2020-6514 | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC. Reported by Natalie Silvanovich of Google Project Zero on 2020-04-30 |
| High | CVE-2020-6515 | Use after free in tab strip. Reported by DDV_UA on 2020-05-14 |
| High | CVE-2020-6516 | Policy bypass in CORS. Reported by Yongke Wang of Tencent’s Xuanwu Lab (xlab.tencent.com) on 2020-06-08 |
| High | CVE-2020-6517 | Heap buffer overflow in history. Reported by ZeKai Wu (@hellowuzekai) of Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab on 2020-06-16 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6518 | Use after free in developer tools. Reported by David Erceg on 2019-07-20 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6519 | Policy bypass in CSP. Reported by Gal Weizman (@WeizmanGal) of PerimeterX on 2020-03-25 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6520 | Heap buffer overflow in Skia. Reported by Zhen Zhou of NSFOCUS Security Team on 2020-06-08 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6521 | Side-channel information leakage in autofill. Reported by Xu Lin (University of Illinois at Chicago), Panagiotis Ilia (University of Illinois at Chicago), Jason Polakis (University of Illinois at Chicago) on 2020-04-27 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6522 | Inappropriate implementation in external protocol handlers. Reported by Eric Lawrence of Microsoft on 2020-02-13 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6523 | Out of bounds write in Skia. Reported by Liu Wei and Wu Zekai of Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab on 2020-05-08 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6524 | Heap buffer overflow in WebAudio. Reported by Sung Ta (@Mipu94) of SEFCOM Lab, Arizona State University on 2020-05-12 |
| Medium | CVE-2020-6525 | Heap buffer overflow in Skia. Reported by Zhen Zhou of NSFOCUS Security Team on 2020-06-05 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6526 | Inappropriate implementation in iframe sandbox. Reported by Jonathan Kingston on 2020-04-24 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6527 | Insufficient policy enforcement in CSP. Reported by Zhong Zhaochen of andsecurity.cn on 2019-08-10 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6528 | Incorrect security UI in basic auth. Reported by Rayyan Bijoora on 2020-03-22 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6529 | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC. Reported by kaustubhvats7 on 2019-06-26 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6530 | Out of bounds memory access in developer tools. Reported by myvyang on 2019-10-21 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6531 | Side-channel information leakage in scroll to text. Reported by Jun Kokatsu, Microsoft Browser Vulnerability Research on 2020-01-17 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6533 | Type Confusion in V8. Reported by Avihay Cohen @ SeraphicAlgorithms on 2020-04-11 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6534 | Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC. Reported by Anonymous on 2020-04-20 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6535 | Insufficient data validation in WebUI. Reported by Jun Kokatsu, Microsoft Browser Vulnerability Research on 2020-04-22 |
| Low | CVE-2020-6536 | Incorrect security UI in PWAs. Reported by Zhiyang Zeng of Tencent security platform department on 2020-05-09 |
Also read: 9 Policies For Security Procedures Examples