KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!





The TrickBot gang operators are increasingly targeting high-value targets with the new stealthy BazarLoader trojan before deploying the Ryuk ransomware.
For years, the TrickBot gang has been using their trojan to compromise enterprise networks by downloading different software modules used for specific behavior such as stealing passwords, spreading to other machines, or even stealing a domain’s Active Directory database.
As these modules have become heavily analyzed over time, security solutions have become better at detecting these modules before being utilized.
In April 2020, we reported that the TrickBot gang had started to use a new BazarLoader/BazarBackdoor infection in phishing attacks.
In a new report, Advanced Intel security researchers explain that instead of burning victims with the highly-detected TrickBot trojan, threat actors now favor BazarBackdoor as their tool of choice for high-value enterprise targets.
Also Read: Limiting Location Data Exposure: 8 Best Practices
“BazarBackdoor remains the covert malware relying upon minimal functionality while on the host producing high-value long-term infections due to its simplicity and external operation dependency to exploit more information later.”
“In other words, the BazarBackdoor “blending-in“ simplicity and obfuscation layer allows the payload to be a better choice for high-value targets,” Kremez told BleepingComputer in a conversation about their report.
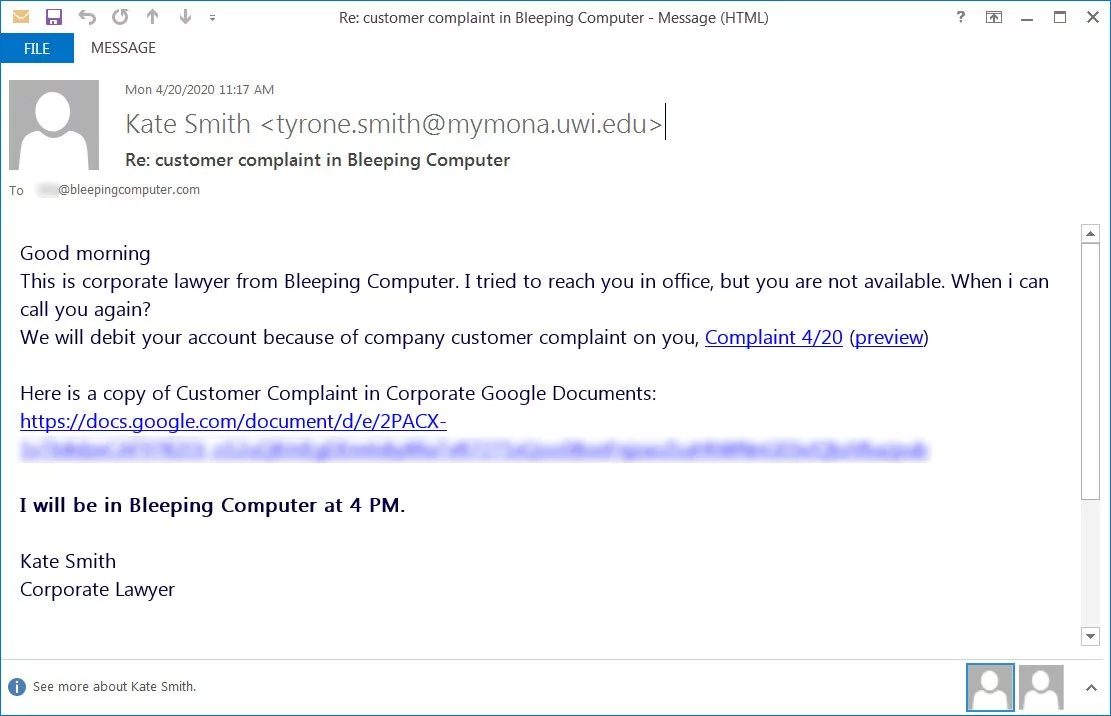
A BazarLoader compromise starts with a targeted phishing attack, as shown by a phishing email received by BleepingComputer in April.
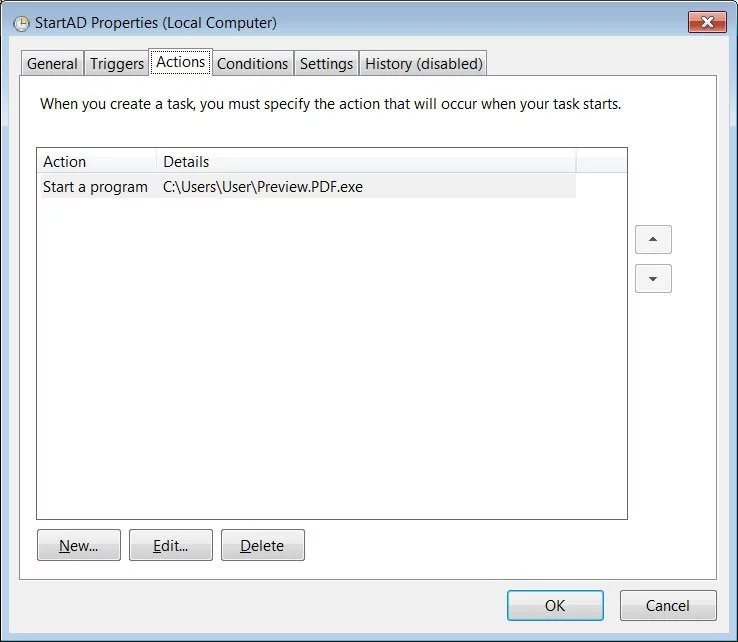
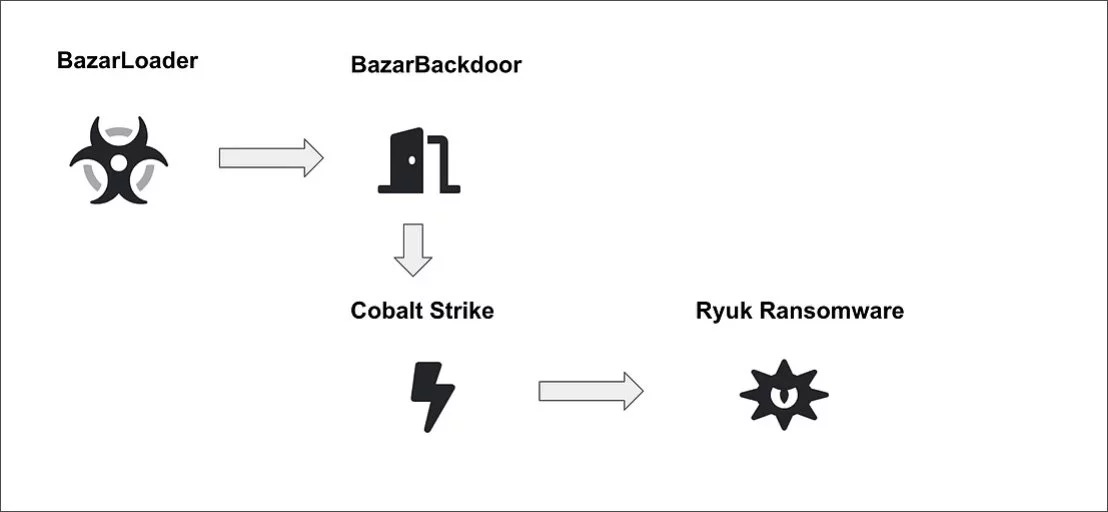
After infecting a computer, BazarLoader will use process hollowing to inject the BazarBackdoor component into legitimate Windows processes such as cmd.exe, explorer.exe, and svchost.exe. A scheduled task is created to load BazarLoader every time a user logs into the system.
Eventually, BazarBackdoor will deploy a Cobalt Strike beacon, which provides remote access to threat actors who install post-exploitation tools such as BloodHound and Lasagne for mapping a Windows domain and extracting credentials.
Ultimately, the attack leads to threat actors deploying Ryuk ransomware on the entire network and demand massive ransoms.
Also Read: 10 Practical Benefits of Managed IT Services
Even with this increase in utilization, as BazarBackdoor requires a more significant amount of human-operation, Kremez believes that BazarLoader will be reserved for select targets.
“The downside of hunting with BazarBackdoor is that it requires an expensive exploitation operation to pivot from the infections,” Kremez explained.
For mass-distribution, we should continue to see TrickBot utilized for network compromise.

Established in 2018, Privacy Ninja is a Singapore-based IT security company specialising in data protection and cybersecurity solutions for businesses. We offer services like vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and outsourced Data Protection Officer support, helping organisations comply with regulations and safeguard their data.
Singapore
7 Temasek Boulevard,
#12-07, Suntec Tower One,
Singapore 038987
Latest resources sent to your inbox weekly
© 2025 Privacy Ninja. All rights reserved
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!

Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!
