KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!







The Apache Software Foundation has released version 2.4.50 of the HTTP Web Server to address two vulnerabilities, one of which is an actively exploited path traversal and file disclosure flaw.
The Apache HTTP Server is an open-source, cross-platform web server that is extremely popular for being versatile, robust, and free. As such, any vulnerability in the product has widespread consequences.
The actively exploited zero-day vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2021-41773 and it enables actors to map URLs to files outside the expected document root by launching a path traversal attack.
Path traversal attacks involve sending requests to access backend or sensitive server directories that should be out of reach. Normally, these requests are blocked, but in this case, the filters are bypassed by using encoded characters (ASCII) for the URLs.
Also Read: Understanding The Data Intermediary In Data Protection
Additionally, exploits of this flaw may lead to the leaking of the source of interpreted files such as CGI scripts.
For the attack to work, the target has to run Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49, and also has to have the “require all denied” access control parameter disabled. Unfortunately, this appears to be the default configuration.
Earlier Apache Server versions or those having a different access configuration aren’t vulnerable to this flaw.
Since the disclosure of the vulnerability, security researchers have been able to reproduce the vulnerability and warned that admins should patch immediately
We have reproduced the fresh CVE-2021-41773 Path Traversal vulnerability in Apache 2.4.49.
If files outside of the document root are not protected by “require all denied” these requests can succeed.
Patch ASAP! https://t.co/6JrbayDbqG pic.twitter.com/AnsaJszPTE— PT SWARM (@ptswarm) October 5, 2021
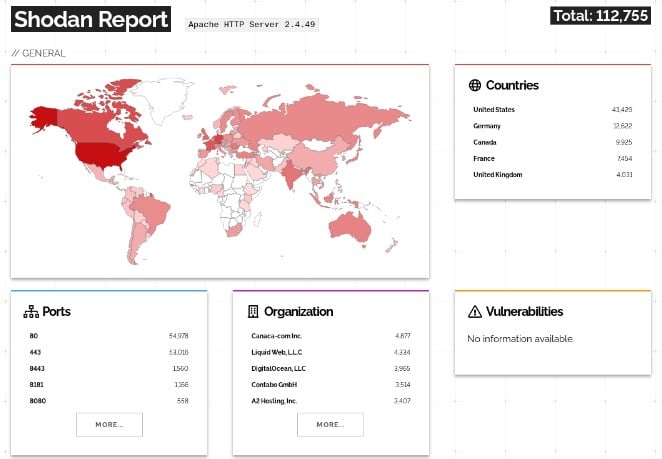
A Shodan search revealed that there are over a hundred thousand Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 deployments online, many of which could be vulnerable to exploitation, so updating your software as soon as possible should be considered exigent.
The vulnerability was discovered and reported to Apache by security researcher Ash Daulton and the cPanel Security Team on September 29, 2021. Being an actively exploited flaw, the fix for it came pretty quickly.
At this time it is not known how the vulnerability is being used in attacks. When we asked Apache for further information, they sent BleepingComputer the following statement:
Also Read: How Being Data Protection Trained Can Help With Job Retention
As Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 was only released a few weeks ago it’s likely many users will not have upgraded yet. If and how this issue can be exploited is highly dependent on how users will have configured the server. If you are using 2.4.49, it is recommended that you upgrade to the latest version instead of using access control configuration as a mitigation. On a default installation, an attacker could still use the flaw to obtain the source code of interpreted files like CGI scripts.
The second vulnerability is CVE-2021-41524, a null pointer dereference detected during HTTP/2 request processing. This flaw allows an attacker to perform a denial of service (DoS) attack on the server.
This flaw too only exists in Apache Server version 2.4.49, but it’s not under active exploitation. It was discovered three weeks ago, fixed late last month, and incorporated now in version 2.4.50.