KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!







A heavily downloaded Node.js library has a high severity command injection vulnerability revealed this month.
Tracked as CVE-2021-21315, the bug impacts the “systeminformation” npm component which gets about 800,000 weekly downloads and has scored close to 34 million downloads to date since its inception.
Put simply, “systeminformation” is a lightweight Node.js library that developers can include in their project to retrieve system information related to CPU, hardware, battery, network, services, and system processes.
According to the project’s developer, developers are expected to use “systeminformation” in the backend.
“Node.js comes with some basic OS information, but I always wanted a little more. So I came up to write this little library.”
“This library is still work in progress. It is supposed to be used as a backend/server-side library (will definitely not work within a browser),” states the developer behind the component.
However, the presence of the code injection flaw within “systeminformation” meant an attacker could execute system commands by carefully injecting payload within the unsanitized parameters used by the component.
The fix shown below that went into version 5.3.1 of “systeminformation” sanitizes the parameters, checks if they are of the string data type and additionally whether prototype pollution had occurred at any point by the parameter, prior to invoking further commands.
Also Read: A Look at the Risk Assessment Form Singapore Government Requires
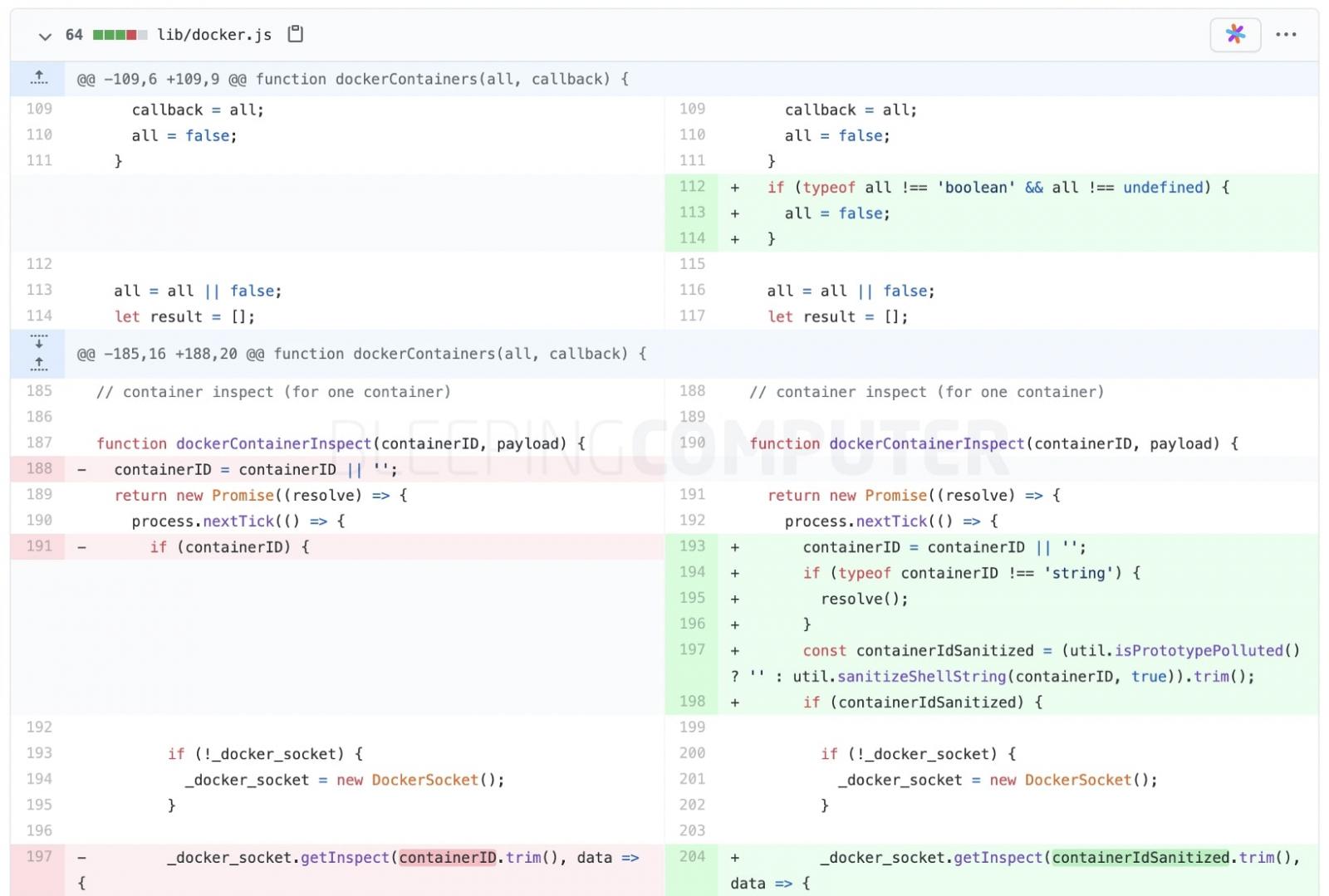
Users of “systeminformation” should upgrade to versions 5.3.1 and above to resolve the CVE-2021-21315 vulnerability in their application.
For developers who are unable to upgrade to the fixed version, the project publisher has shared information on a workaround that can be adopted instead.
This again involves cleaning up the parameters for any offending characters and properly validating if they are of the string data type.
“As a workaround instead of upgrading, be sure to check or sanitize service parameters that are passed to si.inetLatency(), si.inetChecksite(), si.services(), si.processLoad() … do only allow strings, reject any arrays. String sanitation works as expected,” reads the associated npm security advisory.
Node.js developers are encouraged to ensure if their applications properly sanitize user input prior to using it within commands and database queries.
Also Read: How to Send Mass Email Without Showing Addresses: 2 Great Workarounds
Users should also periodically visit npm security advisories for information on the latest security fixes made to Node.js components.