KEEP IN TOUCH
Subscribe to our mailing list to get free tips on Data Protection and Cybersecurity updates weekly!





MountLocker ransomware received an update recently that cut its size by half but preserves a weakness that could potentially allow learning the random key used to encrypt files.
This ransomware operation started in July 2020, and it targets corporate networks. Its operators steal data before encrypting it and threaten victims to leak files unless their multi-million dollar ransom demands are met.
In the second half of November, the second version, malware researchers saw the second version of MountLocker in the wild with clues that its operators are preparing for the tax season.
Research from Vitali Kremez, reverse engineer and CEO of Advanced Intelligence (AdvIntel), shows that the ransomware developers added file extensions (.tax, .tax2009, .tax2013, .tax2014) associated with the TurboTax software for preparing tax return documents.
In a technical analysis published today, the BlackBerry Research and Intelligence Team notes that the new MountLocker variant comes with a compilation timestamp from November 6.
The malware developers reduced the size of the 64-bit malware variant to 46KB, which is about 50% smaller than the previous version. To get to this, they removed the file extension list with more than 2,600 entries targeted for encryption.
Also Read: Computer Misuse Act Singapore: The Truth And Its Offenses
It now targets a much smaller list that excludes easily replaceable file types: .EXE, .DLL, .SYS, .MSI, .MUI, .INF, .CAT, .BAT, .CMD, .PS1, .VBS, .TTF, .FON, .LNK.
The new code is very similar to the old one, the biggest change being the process for deleting volume shadow copies and for terminating processes, which is now done with PowerShell script before encrypting the files.
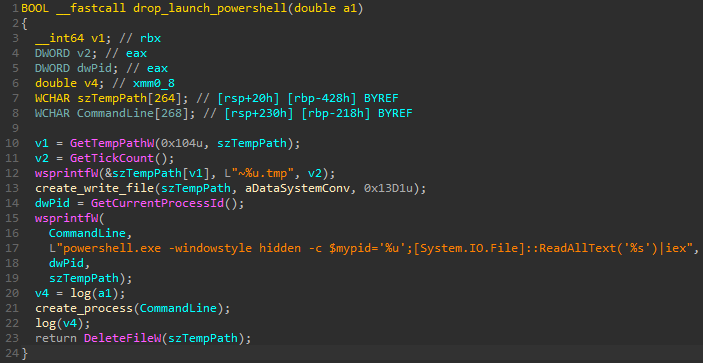
BlackBerry says that 70% of the code in the new MountLocker is the same as in the previous version, including the insecure Windows API function GetTickCount by the malware to generate a random encryption key (session key).
GetTickCount has been deprecated in favor of GetTickCount64. In its list of cryptographic recommendations, Microsoft lists both functions as insecure methods for generating random numbers.
BlackBerry says that the use of the GetTickCount API offers a “slim possibility” to find the encryption keys through brute-forcing.
The researchers add that the success of this endeavor depends on knowing the timestamp counter value during the ransomware execution.
MountLocker encrypts files on the infected computers using the ChaCha20 stream cipher and the session key is then encrypted with a 2048-bit RSA public key embedded in its code.
Like other ransomware operations, MountLocker developers rely on affiliates for breaching corporate networks. The techniques they use are commonly used in ransomware attacks.
BlackBerry’s investigation of MountLocker campaigns showed that the actors are often accessing the victim network via a remote desktop (RDP) connection with compromised credentials.
Cobalt Strike beacons and the AdFind active directory query tool have been observed in these attacks for reconnaissance and moving laterally on the network, while FTP was used to steal files before the encryption stage.
In an incident that BlackBerry analyzed, a MountLocker affiliate gained access to a victim’s network and paused for several days before resuming activity.
The researchers believe that the intruder sit still because they were negotiating with the developers to join the affiliate program.
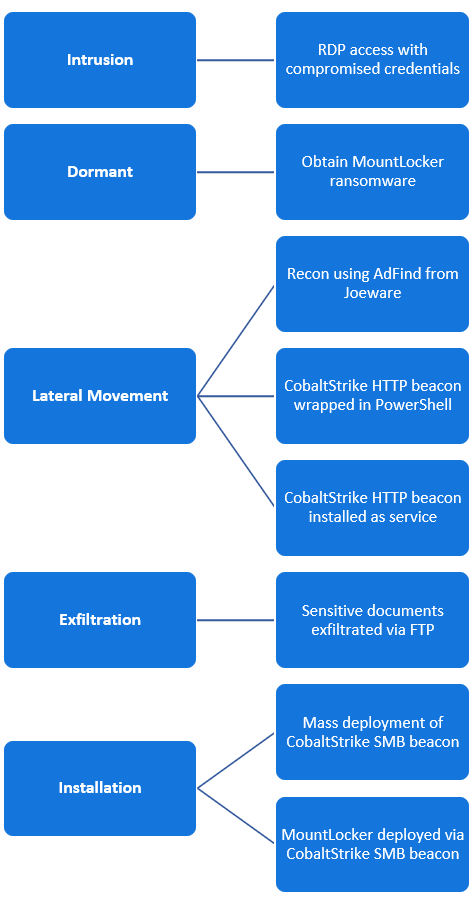
After obtaining the ransomware, the intruder took about 24 hours to run reconnaissance, steal files, move laterally, and deploy MountLocker.
Also Read: Personal Data Websites: 3 Things That You Must Be Informed
BlackBerry researchers say that quick operations like this one are normal in attack from MountLocker affiliates as they can steal data and encrypt key machines on the network in hours.
Despite being new, this strain of ransomware is clearly after big money and is likely to expand operations for maximum profit. Its leak site currently lists a handful of victims that did not pay but the number is much larger.
Even if the group behind it is not “particularly advanced” at the moment, the researchers expect it to continue its effort over the short term.